POLICY CENTER FOR THE NEW SOUTH
Otaviano Canuto and Amshika Amar
Introduction
When international locations face exterior monetary shocks, they have to depend on monetary buffers to counter such shocks. The worldwide monetary security internet is the set of establishments and preparations that give economies layers of protection in opposition to such shocks.
From any particular person nation standpoint, there are three layers or strains of protection of their exterior monetary monetary security nets (Iancu et al, 2021). The primary is the international locations’ personal worldwide reserves. A second line of protection comes from pooling assets with different international locations. Bilateral swap strains, whereby central banks trade currencies to supply liquidity to monetary markets, is a possible protecting layer. Moreover, plurilateral—regional or not—financing preparations, by which international locations pool assets to answer financing wants in a shock, additionally supply a line of protection. Lastly, there may be the Worldwide Financial Fund (IMF), as a multilateral lender of resort.
The second line of protection—swap strains and plurilateral financing preparations—has been enhanced over the previous twenty years. Nonetheless, this safety stays obtainable solely to a small group of nations.
We argue right here that there’s a want to increase and facilitate entry to the final word world monetary security internet layer—the IMF. We illustrate this by stating how Morocco and Mexico have boosted their defensive energy by getting access to IMF precautionary strains of credit score.
Worldwide Reserves are the First Line of Exterior Monetary Protection
A rustic’s worldwide reserves are its first line of protection. Holding worldwide reserves is dear, as their asset returns are low. Their non-use to acquire various kinds of belongings corresponds to a chance price, one that’s in precept justified by the features from safety in opposition to shocks and stoppage of transactions. A really hard-to-answer query is what the optimum ranges of reserves are to be able to preserve a stability between such prices and advantages (Saraiva and Canuto, 2009).
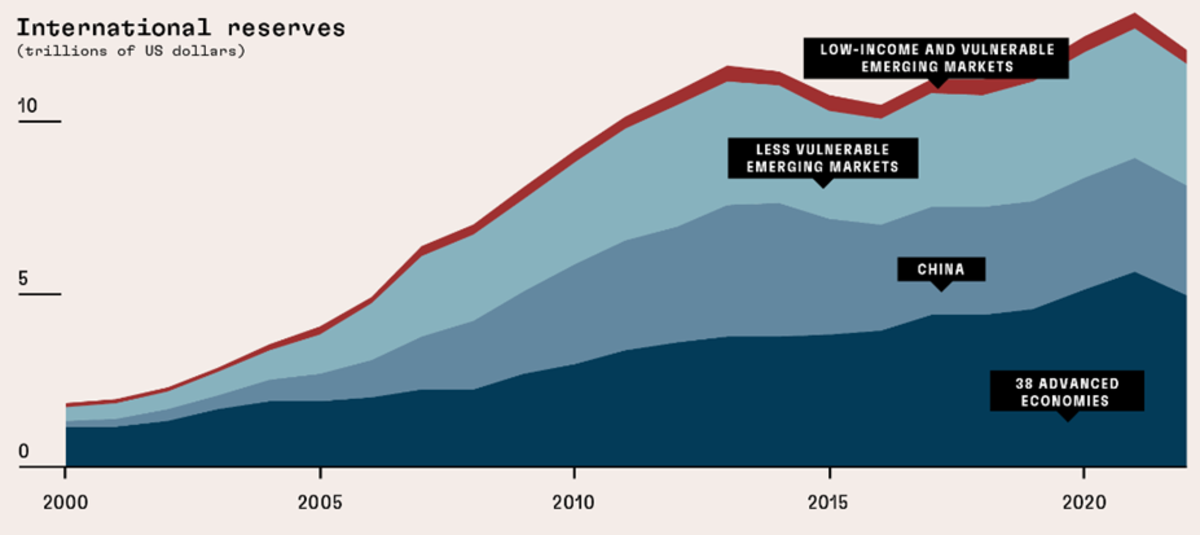
Nations’ worldwide reserves have grown in quantity lately, after a dip within the second half of the 2010s (Determine 1). Nonetheless, the mixture numbers cover a really variable image amongst particular person international locations. As identified by Stanley (2023), 97% of these reserves have been amassed by roughly 50% of nations, whereas round 90 rising market and low-income international locations account for the remaining 3% or reserves. Whereas many rising market economies considerably elevated their worldwide reserves within the 2000s (Canuto and Cavallari, 2017), that has not been the case of most low-income international locations.
Determine 1: Worldwide Reserves
Pooling Assets Constitutes a Second Line of Protection
Pooling assets—through bilateral swap strains and regional or plurilateral preparations—is an extra protect in opposition to shocks. Swap strains are preparations which can be designed to enhance liquidity situations and assist ease pressure in monetary markets. They assist monetary stability and function a prudent liquidity backstop (Determine 2).
Determine 2: International Monetary Security Web
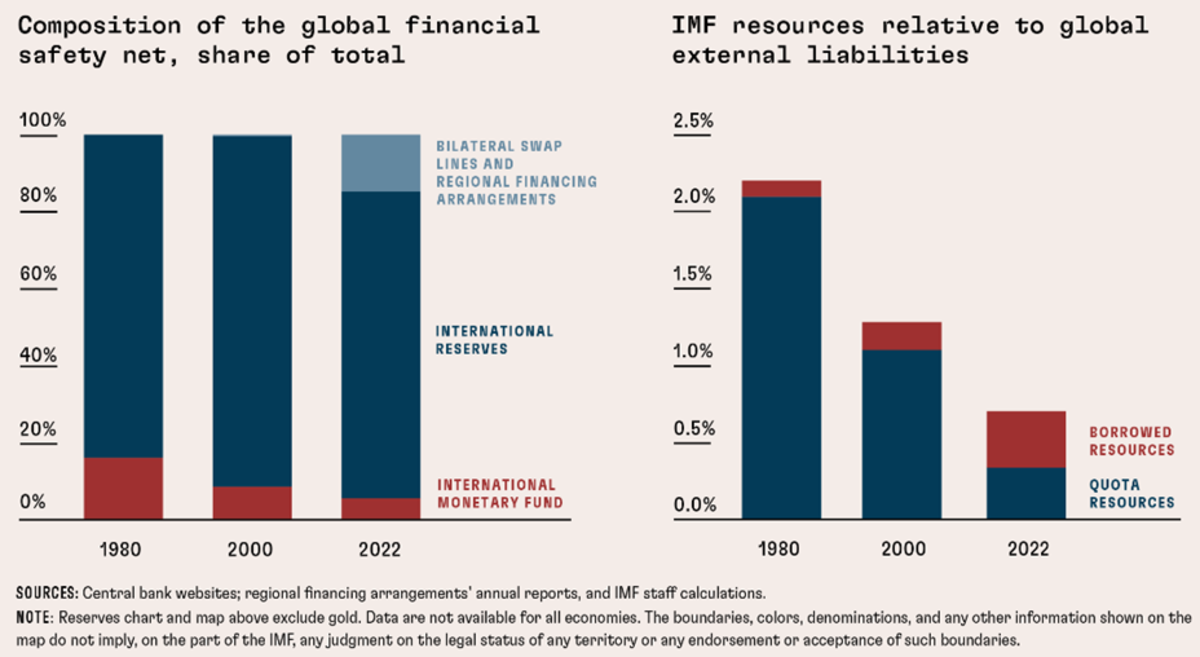
Supply: Stanley (2023).
Allow us to illustrate the elevated weight of this second line of protection by wanting on the Federal Reserve and the European Central Financial institution (ECB). The U.S. Federal Reserve operates greenback swap strains with the next central banks: Reserve Financial institution of Australia, the Financial institution of Canada, Danmarks Nationalbank, the Financial institution of England, the European Central Financial institution, the Financial institution of Japan, the Financial institution of Korea, the Banco de Mexico, the Reserve Financial institution of New Zealand, Norges Financial institution, the Financial Authority of Singapore, Sveriges Riksbank, and the Swiss Nationwide Financial institution. The very best greenback transaction by way of swap strains is with the ECB ($814 billion). The one rising market with such a transaction is Mexico ($15 billion). Most swap strains have been used through the COVID-19 pandemic.
The Federal Reserve additionally operates foreign-currency liquidity swap strains with the Financial institution of Canada, the Financial institution of England, the Financial institution of Japan, the European Central Financial institution, and the Swiss Nationwide Financial institution.
The ECB, in the meantime, is a part of a swap-line community of standing bilateral preparations with 5 different main central banks (the Financial institution of Canada, the Financial institution of Japan, the Swiss Nationwide Financial institution, the Financial institution of England, and the Federal Reserve System). The ECB has more and more used swap and repo strains because the 2008-09 world monetary disaster.
The ECB supplies euro in opposition to foreign exchange, that are accepted as collateral. Underneath reciprocal swap strains, the ECB may additionally obtain foreign exchange by offering euro as collateral. Underneath the repurchase agreements, the ECB supplies euros to non-euro space central banks and receives euro-denominated monetary belongings as collateral.
These swap and repo strains assist meet the liquidity wants of euro and non-euro international locations to stop spillback results that may have an hostile impression on the graceful transmission of the ECB’s financial coverage from impacting on euro-area monetary markets and economies.
The ECB makes use of a strict set of standards when deciding whether or not to grant swap and repo strains to non-euro central banks. In June 2020, the ECB established a short lived Eurosystem repo facility for central banks (EUREP), which goals to broaden entry past the swap and repo strains.
As proven by Determine 2, the second line of protection has emerged because the flip of the millennium. However like worldwide reserves, swap strains are out of attain for a lot of rising market and creating economies. Additionally, the relative dimension of the IMF has diminished, together with relative to world exterior liabilities (Determine 2, proper panel).
Whereas superior economies have established such bilateral swap strains between their central banks to spice up their international liquidity defenses in opposition to shocks, rising market and creating economies (EMDEs) have restricted entry to comparable preparations to assist alleviate their international trade liquidity shortages. Solely a handful of EMDEs have entry to swap strains with advanced-economy central banks.
EMDEs have as a substitute tended to depend on piling up foreign-exchange reserves as a type of self-insurance. Self-insurance is neither individually nor collectively optimum, and this has prompted discussions a couple of extra strong, multi-layered, world monetary security internet.
A number of EMDE central banks have swap strains with the Folks’s Financial institution of China, though the non-convertibility of the renminbi limits the worth of those swap strains (Canuto, 2023a) – see Determine 3. The template provided by China goals at facilitating bilateral commerce and funding, slightly than provision of a security internet. Nonetheless, Argentina was in a position to make the most of its foreign money swap line with China in 2023 to beat difficulties in complying with its debt service obligations with the IMF (Wang and Canuto, 2023).
Determine 3: Evolution of PoBC Swap Strains (RMB trillions)
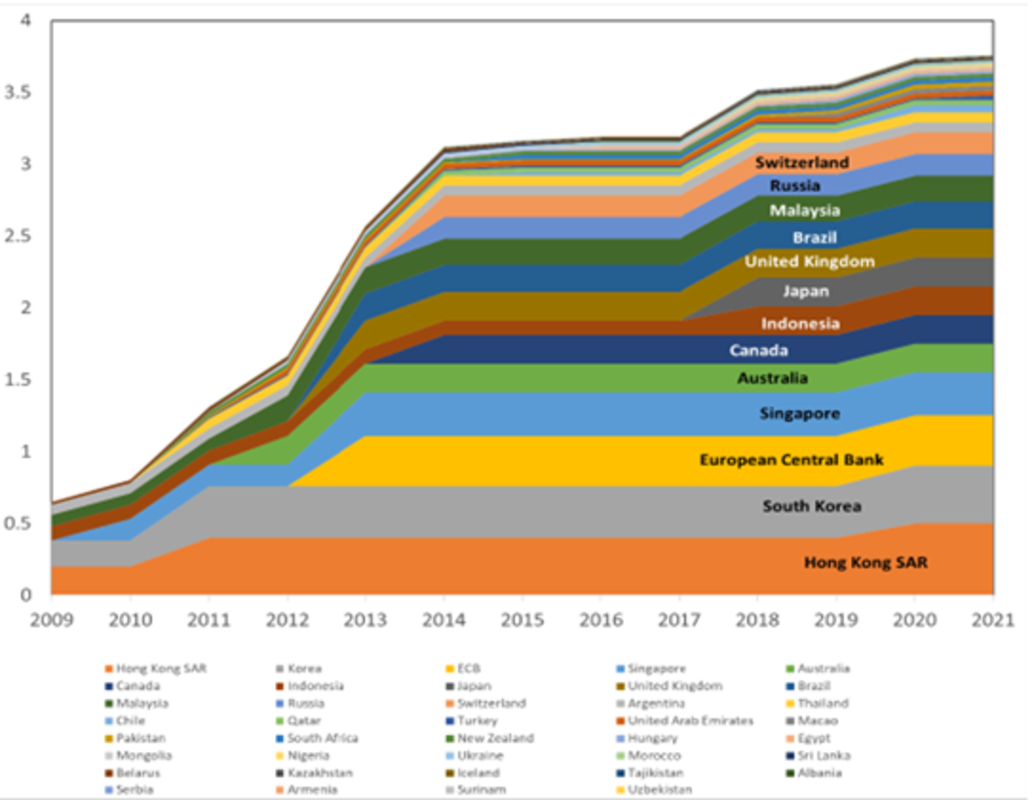
Supply: Bloomberg.
The Position of the IMF because the Core of the International Monetary Security Web
The IMF supplies the broadest and most normal layer of protection in opposition to shocks, whereas—as now we have mentioned—international locations differ very a lot of their potential to resort to first and second strains of protection. Nonetheless, the IMF’s lending capability as a share of worldwide exterior liabilities has shrunk over time (Determine 2), and the share of borrowed assets has elevated (Stanley, 2023).
A sequence of shocks has develop into a function of latest instances, constituting a ‘good storm’ (Canuto, 2023b): the pandemic, warfare in Ukraine and Gaza, local weather change, and geopolitical uncertainty. A key mission of the IMF is to assist members handle balance-of-payments wants generated by such shocks.
Uneven entry to the International Monetary Security Web (GFSN) has important implications for the design of the Fund’s precautionary devices. The Versatile Credit score Line (FCL) was established on the top of International Monetary Disaster (GFC) to assist international locations handle systemic dangers such because the GFC and the European sovereign debt disaster. It was assumed that, following the decision of those systemic dangers, the sample of shocks to the worldwide buying and selling and monetary system would revert to that prevailing earlier than GFC. The last word goal for the FCL was to sign a rustic’s potential to entry IMF assets with out the necessity for an adjustment program. The Precautionary and Liquidity Line (PLL), in the meantime, is designed to fulfill the liquidity wants of member international locations with sound financial fundamentals, however with some remaining vulnerabilities that require ex-post conditionality and stop them from utilizing the FCL.
The IMF has established a Quick-Time period Liquidity Line (SLL) as a liquidity backstop for international locations with sturdy coverage frameworks that face potential reasonable, short-term liquidity wants. It goals to reduce the chance of shocks evolving into deeper crises and spilling over to different international locations. The SLL has not been totally utilized by any nation but. Chile had an SLL from Could by way of September 2022, however reverted to the FCL.
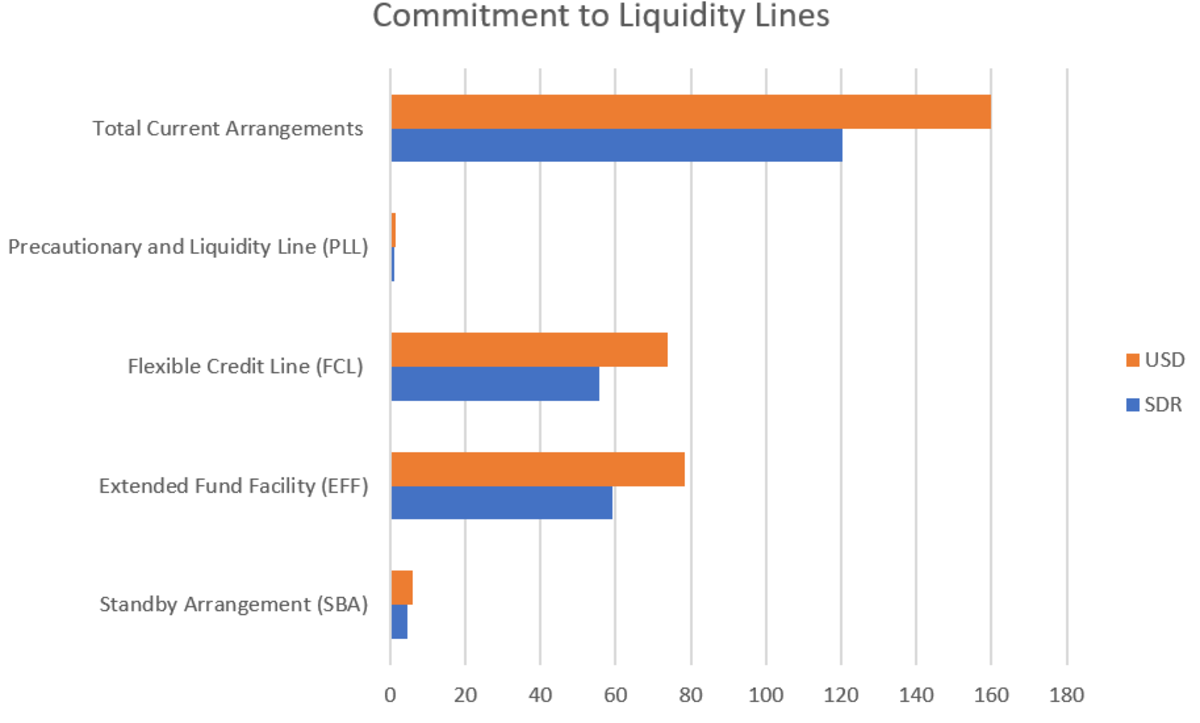
The IMF has deployed $1 trillion in world liquidity and reserves by way of its lending because the pandemic and the 2021 allocation of $650 billion in Particular Drawing Rights (SDRs). Via the Poverty Discount and Development Belief, interest-free financing to 56 low-income international locations has been offered (Determine 4). As of September 2023, the IMF had lending commitments with 94 international locations for about $287 billion, or SDR 218 billion. This included: precautionary amenities for seven rising market economies for $93 billion; lending commitments to 35 rising market economies for $134 billion; interest-free lending of $23.5 billion for 45 low-income international locations; $30.5 billion of excellent credit score associated to emergency financing for 77 international locations; .
Determine 4: IMF Lending Instruments
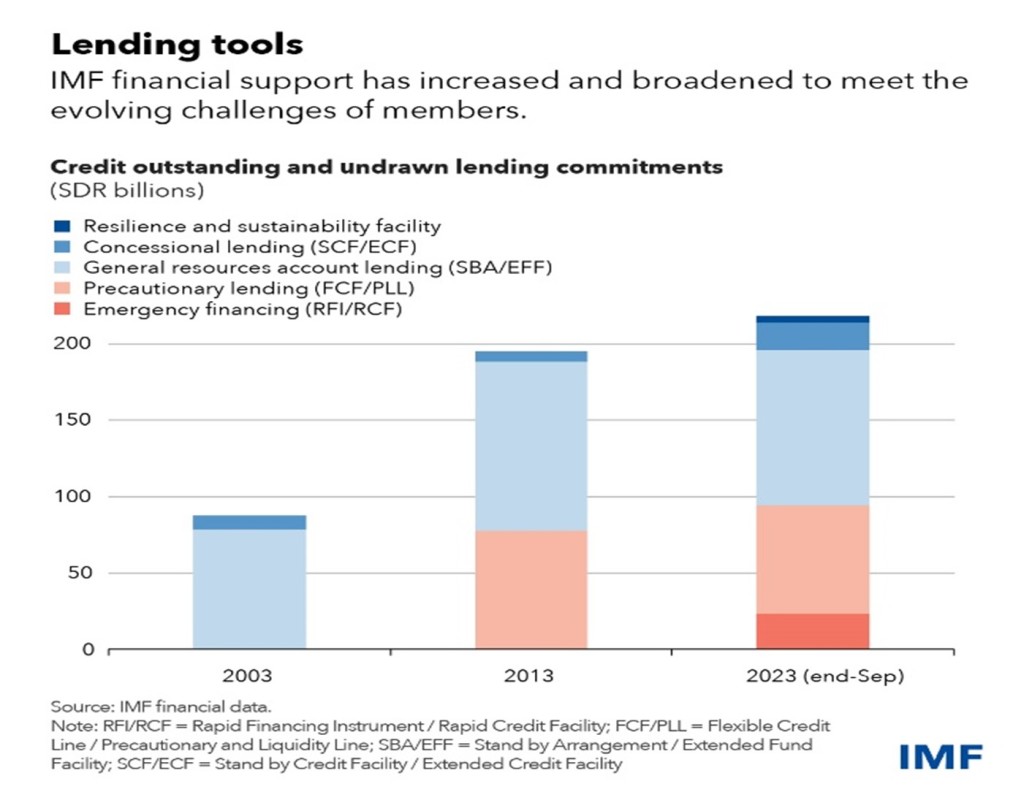
Supply: IMF.
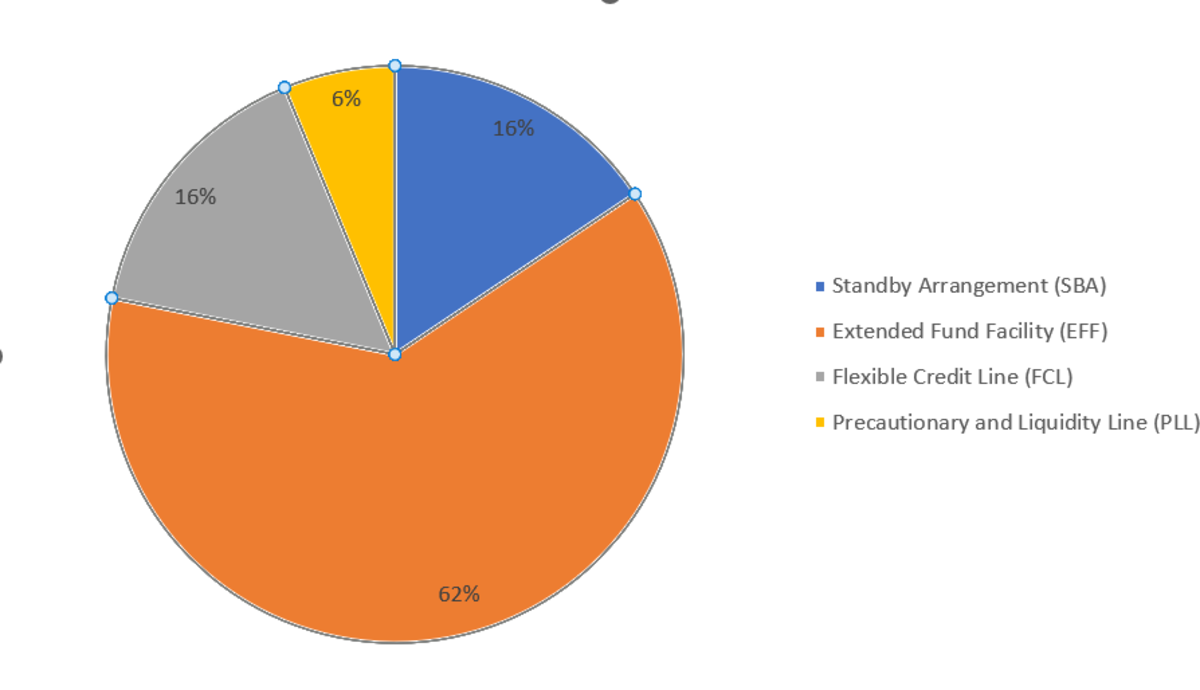
The IMF’s precautionary devices—the FCL and the PLL—stay underutilized (Figures 5 and 6). At time of writing, solely 5 international locations—Colombia, Mexico, Chile, Peru, and most lately Morocco—have entry to the FCL.
Morocco has benefited from a PLL line since 2012 and was the one nation to attract on it and use it to fund its liquidity wants through the pandemic in April 2020. Subsequently, Morocco began negotiations with the IMF and concluded an settlement giving it entry to the FCL. The primary PLL helped Morocco stabilize its home T-Payments and foreign-exchange markets, at a time when rates of interest have been trending upward, and the Moroccan foreign money was beneath devaluation strain.
There are at present two PLLs (Jamaica and North Macedonia). This represents a major improve from two FCLs and one PLL earlier than the pandemic. There is no such thing as a cap on the funds obtainable beneath the FCL, whereas beneath PLL, member states can entry as much as 500% of their quota.
Determine 5: Share Values of Numbers of Liquidity Strains
Supply: IMF Report on Key Monetary Statistics as of December 2023.
Determine 6: Dedication to Liquidity Strains
Supply: IMF Report on Key Monetary Statistics as of December 2023.
The IMF has proposed the next modifications beneath the evaluation of the FCL, SLL and PLL:
a) An SLL-FCL reform bundle that permits for mixed (FCL and SLL) entry of as much as 400% of quota with out the articulation of exit expectations;
b) SLL-FCL concurrent use—the concurrent use of FCL and SLL ought to be permitted. The procedures to make preparations extra simply usable and versatile ought to be streamlined; for instance, the variety of board conferences wanted for the evaluation of FCL/PLL with Article 1V ought to be diminished.
The 2011 evaluation of the FCL and PCL discovered a decline in sovereign spreads, following the announcement of recent FCL association (IMF, 2023). The 2014 evaluation of the FCL confirmed that bulletins of a brand new precautionary association resulted in greater capital inflows and decrease sovereign spreads.
The demand for precautionary preparations will improve as world shocks develop into multifaceted and world liquidity much less simply obtainable. The 2023 evaluation of the FCL confirmed that bulletins of FCL or PLL result in declines in sovereign spreads. The evaluation discovered that there was a big drop in sovereign spreads for FCL customers, starting from 17 to 24 foundation factors, within the first seven buying and selling days following the bulletins (IMF, 2023).
The evaluation discovered that FCL and PLL preparations additionally helped mitigate exterior monetary pressures through the COVID-19 pandemic. After controlling for country-specific results, time results, and world and home drivers of sovereign spreads, international locations with FCL or PLL preparations through the pandemic skilled smaller will increase in spreads, relative to different rising market economies. Sovereign spreads have been about 7% decrease in international locations with an FCL or PLL association, in comparison with different EMEs, confirming the essential position of precautionary preparations in cushioning exterior financing pressures.
Precautionary preparations may also be cheaper than holding reserves when used on a precautionary foundation. They play a complementary position to different layers of the GFSN by providing swift availability of financing when a shock hits. The October 2023 evaluation additionally referred to as for reforms to the FCL and SLL, permitting the 2 devices to higher complement one another.
Birdsall et al (2017) offered proof that the PLL and FCL are among the many least pricey and most advantageous devices for liquidity assist to international locations, and that the financial impression following agreements on an FCL or PLL has been constructive in all circumstances. On the time of their analysis, their evaluation offered proof that there have been a minimum of 18 further IMF members that may qualify for an FCL, and several other extra can be eligible for PLL. Because the IMF’s dedication standards for a member state’s eligibility is ambiguous, it serves as a disincentive for brand spanking new purposes. There may be additionally ambiguity concerning the share of assets the IMF is prepared to dedicate to precautionary lending.
Since there isn’t any ex-post conditionality hooked up to FCL, and really restricted conditionality hooked up to PLL, the 2 credit score strains characterize a departure from the IMF’s conventional lending practices. Any main shareholders that will resist such facilitation ought to be satisfied of its advantages.
The Evolution of Overseas Foreign money Credit score
The worldwide monetary security internet should sustain with the evolution of economic intermediation (Carstens, 2021). The rise in U.S. dollar-denominated worldwide debt securities was a powerful pattern within the final decade. It mirrored an growing position performed by non-bank monetary establishments (NBFIs) and market-based finance, whereas U.S. dollar-denominated cross-border financial institution loans shrank as a share of worldwide GDP (Canuto, 2023c).
Certainly, world liquidity—the convenience of financing in worldwide monetary markets—has a key side, which is international foreign money credit score (FCC), a variable that has undergone distinct phases in latest historical past (Hardy and von Peters, 2023). The primary part (2003-09) was recorded by Financial institution for Worldwide Settlements world liquidity indicators that includes hovering financial institution credit score, which comprised cross-border credit score and credit score in international foreign money. This worldwide credit score evaporated shortly because the GFC hit, exposing monetary vulnerabilities in each superior and rising market economies.
Beginning within the early 2000s and main as much as the GFC, the primary part of worldwide liquidity noticed a big enlargement in FCC. The mixed inventory of foreign-currency credit score in {dollars}, euros, and yen doubled from $5 trillion in Q1 2003 to $10 trillion in Q1 2008 (). As a share of world GDP, it rose from 13% to a peak of 17%. This dramatic development was pushed by the speedy enlargement within the worldwide actions of banks. A permissive macro-financial and coverage atmosphere led to this growth in world liquidity.
The second part (2009-21) noticed a shift in direction of bond markets and extra greenback credit. This part started within the aftermath of the GFC and featured a shift to bond-market credit score as a consequence of tighter regulation of banks. Greenback credit score expanded essentially the most, specifically to debtors in rising market economies.
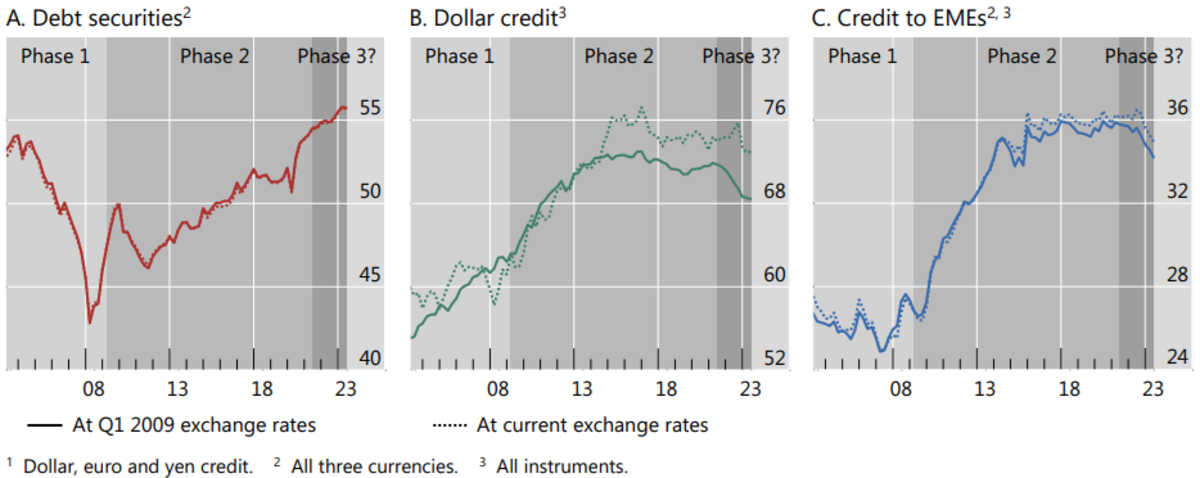
The defining function of the second part of worldwide liquidity was the shift in direction of bond markets. The share of foreign-currency credit score within the type of bonds rose from a trough of 43% in Q1 2008, to 55% by end-Q2 2021 (Determine 7-A). The greenback, already the dominant foreign money, noticed an extra rise in its share in world credit score markets (Determine 7-B). Credit score to rising market debtors took heart stage, with their share in FCC rising from 26% in Q2 2009 to 36% by end-2015 (Determine 7-C).
Determine 7: Composition of International Liquidity: As a % of Complete Overseas Foreign money Credit score to Non-bank Debtors
Supply: Hardy and von Peter (2023).
Hardy and von Peter (2023) urged a 3rd part of that evolution in world liquidity could also be underway. FCC has begun to contract in combination. This credit score as a share of worldwide GDP fell from 20% on the end-Q2 2021 to 17% at end-Q2 2023.
The expansion of credit score from bond markets slowed to a standstill from mid-2021 onward, however its share saved rising as a result of financial institution lending declined. Whereas the drop in greenback lending by emerging-market banks was notably sharp, banks of assorted nationalities drove the decline in lending.
Greenback-denominated credit score witnessed a steeper contraction, matching the tighter stance of U.S. financial coverage in contrast with that of the euro space and Japan. In Q3 2021, the year-on-year development in greenback credit score was 6%, falling to minus 4% on the finish of 2022. Nonetheless, euro credit score development slowed, and yen development accelerated over the identical interval. Evaluated at fixed trade charges, the greenback shares of international foreign money credit score declined from 72% in mid-2021 to 68% by mid-2023.
Credit score to rising market debtors declined much more steeply than general credit score. On the finish of Q2 2023, euro credit score to rising market debtors shrank by 2% year-on-year, at the same time as euro credit score continued to broaden. By mid-2023, greenback credit score—the predominant international funding foreign money for many rising market economies—shrank by 5% year-on-year.
Geopolitical uncertainty and geoeconomic fragmentation might additional tighten credit score situations (Canuto, 2023b, 2023d). Monetary vulnerabilities constructed up through the second part, notably for the EMDEs which can be closely depending on international foreign money debt, could possibly be uncovered by a sustained tightening of credit score situations.
Nation Case Illustrations From Mexico and Morocco
For Mexico, FCL serves as an essential buffer. On November 15, 2023, a successor two-year association for Mexico beneath the FCL was accepted. Mexico was the primary IMF member to signal an FCL when it was launched in 2009. Although to this point FCL has been handled as precautionary, it has offered Mexico with a considerable buffer. FCL doesn’t contain any post-approval conditionality, implying that the nation can request disbursement anytime as soon as the credit score line is accepted.
FCL, along with worldwide reserves and swap strains with the U.S. Treasury and Federal Reserve, has helped to anchor market confidence in Mexico’s macroeconomic insurance policies. The primary line of protection for Mexico contains floating trade charges and reserves which have served it nicely. FCL supplies an extra exterior buffer in opposition to dangers and has contributed to stronger market confidence.
One can’t predict when liquidity shortages occur, however after they do, world capital pipelines freeze up, making a short-term liquidity downside. Mexico has entry to worldwide capital markets with a sovereign ranking from Moody’s at Baa2 in 2022, S&P at BBB in 2022, and Fitch at BBB- in 2023, that means it retains funding grade standing, in response to all three companies.
In 2022, gross worldwide reserves stood at $202 billion, which exceeds any normal metric of reserve sufficiency. On the finish of 2021, the U.S. Federal Reserve’s non permanent COVID-19-related swap strains expired. However Mexico retains the swap line of $3 billion with the Federal Reserve that’s related to the North American Framework Settlement, and a $9 billion swap line with the U.S. Treasury. Mexico additionally has entry to SDR 8.5 billion, as of 2023.
For Morocco, in the meantime, though the nation has proved resilient within the final decade within the face of cumulative shocks, and has succeeded in sustaining macroeconomic stability, the worldwide financial and geopolitical panorama can alter swiftly and stress even additional the home financial state of affairs. There’s a rising prominence of ‘geo-economics’ and the accompanying position of onerous and delicate infrastructure. A lot of the infrastructure improvement over the previous years has been directed at reinforcing Morocco’s sturdy orientation in direction of Europe and European markets. There has additionally been an growing thrust within the nation to diversify its set of companions and broaden it additional. Significantly in focus have been sub-Saharan Africa, the Gulf Nations, and america.
Morocco is caught in a dependent financial partnership with Europe making it weak to financial shocks in Europe. It could possibly be affected by financial fallout from Russia’s warfare in Ukraine by way of decrease exterior demand (particularly from the euro space). Additionally it is topic to important draw back dangers, together with geopolitical dangers and unstable world monetary situations and commodity costs, notably vitality costs.
The EU neighborhood coverage envisions a powerful dedication to provision of help to North Africa, but in addition individualized approaches in direction of Egypt, Tunisia, and Morocco, together with by way of free commerce with southern Mediterranean companions and large-scale funding in regional infrastructure tasks.
Morocco’s present account deficit in 2023 corresponded to 1.6% of GDP, in response to central financial institution estimates, and is at present projected to deteriorate to three.1% of GDP by 2027. The commerce deficit additionally elevated to 16.5% of GDP in 2022. FDI inflows have helped fund the exterior financing wants. Morocco’s worldwide reserves in U.S. {dollars} have declined, reflecting the depreciation of the euro in opposition to the greenback (60% of Morocco’s reserves are in euros).
It stays essential to protect foreign-exchange reserves in order that they will present a buffer in opposition to uncertainty and Morocco’s pegged exchange-rate regime with horizontal bands (+/- 5%). Although there was a rise in lending from bilateral and multilateral lenders, the authorities have to diversify their financing sources and entry worldwide monetary markets. Morocco accessed the worldwide monetary market in March 2023, one of many few international locations in Center East and North Africa to do it within the present turbulent context.
Financial institution Al-Maghrib (BAM) also needs to transfer ahead to the ultimate phases of transition to an inflation-targeting framework, and permit the dirham to drift freely, which might strengthen Morocco’s resilience in opposition to future shocks. Morocco’s central financial institution envisions reaching this reform by 2027, in response to its 2024-2027 strategic plan.
In step with the suggestions made by the IMF in its newest Monetary Sector Evaluation Program (FSAP) of Morocco, progress has been made by growing supervisory capability and bettering BAM’s stress testing and macroprudential coverage framework with technical help offered by the IMF. The oversight of Moroccan banks increasing into Africa has intensified, in shut collaboration with supervisory companies in host international locations. From February 2020 to the top of 2020, there was a have to immediately assist corporations beneath financing constraints, and to answer rising demand for liquidity within the banking system (each in home and international foreign money), in addition to a name for an enlargement of the liquidity provision to the banking sector. This may be achieved by way of extra refinancing operations by BAM.
The PLL association offered helpful insurance coverage in opposition to exterior shocks whereas bolstering investor confidence. PLL is handled as precautionary and is barely drawn on within the occasion of unexpected exogenous shocks. Since 2012, Morocco had 4 successive PLL preparations. In 2012, a two-year PLL association amounting to SDR 4.12 billion was accepted. This was adopted by successive two-year PLL preparations: one with entry to SDR 3.2351 billion accepted in 2015, and one other with entry to SDR 2.504 billion, accepted in 2016. In 2018, a fourth two-year PLL association was accepted, amounting to SDR 2.15 billion. Through the COVID-19 pandemic, in April 2020, Moroccan authorities bought all obtainable assets beneath the PLL association (which is round 3% of GDP), to be able to preserve official reserves. The authorities made an early repurchase of SDR 650 million after the nation issued U.S. dollar-denominated bonds. In consequence, SDR 1.4998 billion stays excellent as of January 2024.
In April 2023, the IMF accepted a two-year association for Morocco beneath the FCL designed for disaster prevention, price about $5.0 billion, equal to SDR 3.7262 billion. Morocco’s sturdy institutional coverage frameworks justified the transition to an FCL association, and this has taken place. The FCL will assist in accelerating the implementation of the structural reform agenda, improve Morocco’s exterior buffers and supply the nation with additional insurance coverage in opposition to danger.
Morocco’s sovereign ranking was Ba1 in 2022 in response to Moody’s, BB+ since 2021 in response to S&P, and BB+ in 2023, in response to Fitch—non-investment grade ranges. Nonetheless, in March 2023, Morocco was in a position to problem two dollar-denominated bonds, with 5 and ten-year maturities, every for $1.25 billion with favorable spreads, reflecting excessive demand from worldwide traders. Morocco solely has entry to SDR 857.2 million.
Nonetheless, the principle level is that, like Mexico, Morocco’s strains of protection in opposition to shocks have been enhanced by the transition to an FCL.
The Backside Line: The ‘International’ A part of the GFSN Wants Boosting
There stay weaknesses within the world monetary security internet for rising markets and creating economies, notably for these unable to build up massive worldwide reserves. These will stay topic to capital-flow and exchange-rate volatility, whereas the reliance on FCC will proceed to be a supply of vulnerability. There may be subsequently an general have to strengthen the worldwide monetary security internet, by strengthening IMF liquidity provision and widening the monetary security internet. Addressing capital-market volatility also needs to be pursued (UN, 2023).
To strengthen liquidity provision and widen the monetary security internet, UN (2023) urged a number of reforms, amongst which:
– Increase the perform and function of SDRs by allocating them based mostly on want, as a substitute of quota multiples.
– Make IMF lending extra versatile, with fewer conditionalities and entry limits, and the removing of surcharges. Quotas and useful resource contributions ought to be delinked from lending. This may bolster the capability to guard in opposition to future crises, supporting members with smaller monetary buffers, who most want such buffers.
– Set up a multilateral currency-swap facility, offering liquidity at low price.
A revamped world monetary security internet ought to embrace further assets for the IMF in addition to reforms. The rise within the IMF’s quota-based assets agreed in 2023 has been a step in that course, however as famous above, there may be nonetheless some strategy to go to reestablish the IMF because the actually world layer of exterior monetary safety.
The IMF’s governance construction should additionally improve its legitimacy, bettering its primary quota formulation of structure. Aligning the distribution of quotas with the present traits of the world economic system is key (Coulibaly and Prasad, 2023).
Lastly, the IMF ought to simplify the modalities for augmenting entry beneath FCL, as a higher variety of rising economies with entry to precautionary lending would make the system extra secure. As said by Brazil’s Minister of Finance, Fernando Haddad, on the Worldwide Financial and Monetary Committee assembly in October 2023, in Marrakech:
“Precautionary preparations are key devices to foster world prosperity and monetary stability. (…) Precautionary amenities assist align incentives in direction of good insurance policies and reinforce stable establishments. The modifications that have been lately adopted by the IMF Govt Board represent an important step in the correct course, by making using these amenities extra engaging, with out decreasing the qualification standards, in order to not weaken the sign. Specifically, the concurrent use of the FCL and the SLL and the non-presumption of exit from low-access FCL will assist make these amenities an integral function of a more practical world monetary security internet, with a stronger give attention to prevention slightly than remediation.”
The worldwide monetary security internet must be bolstered, particularly when it comes to its capability to assist rising markets and creating economies.
References
Birdsall, N.; Rojas-Suarez, L., and Diofasi, A. (2017). Increasing International Liquidity Insurance coverage by way of Precautionary Lending: What the IMF can do. CGD – Heart for International Improvement.
Canuto, O., and Cavallari M. (2017). The Mist of Central Financial institution Stability Sheets, Coverage Temporary PB-17/07, February.
Canuto, O. (2021). Helicopter Reserves to the Rescue, Coverage Heart for the New South, September 1.
Canuto, O. (2023a). Rising Use of Native Currencies in Cross-Border Funds, Coverage Heart for the New South, August 29.
Canuto, O. (2023b). Resilience and Realignment of International Commerce, Coverage Temporary PB – 44/23, November.
Canuto, O. (2023c). “Capital flows and rising market economies because the world monetary disaster”, In Gevorkyan, A.V. (ed.), Overseas Alternate Constraint and Growing Economies, Edward Elgar.
Canuto, O. (2023d). Development Implications of a Fractured Buying and selling System,
Carstens, A. (2021). Rethinking the worldwide monetary security internet, Speech on the Sixth Excessive-Degree Regional Financing Preparations (RFA) Dialogue, October 12.
Coulibaly, B., and Prasad, E. (2021). International liquidity insurance coverage: a proposal to strengthen the monetary security internet, The Banker, October 15.
IMF – Worldwide Financial Fund (2023). Assessment of the Versatile Credit score Line, The Quick Time period Liquidity Line and the Precautionary and Liquidity Line, and Proposals for Reform, October.
Hardy, B. and von Peter, G. (2023). International liquidity: a brand new part, BIS Quarterly Assessment, December.
Iancu, A.; Kim, S.; and Miksjuk, A. (2021). International Monetary Security Web—A Lifeline for an Unsure World, IMF Weblog – Chart of the Week, November 30.
Saraiva, B., and Canuto, O. (2009). Vulnerability, Alternate Price and Worldwide Reserves: Whither Brazil? Roubini EconoMonitor, September 21.
Stanley, A. (2023). International Monetary Security Web, IMF – Finance and Improvement, December.
UN – United Nations (2023). Our Widespread Agenda Coverage Temporary 6: Reforms to the Worldwide Monetary Structure, Could.
Wang, X., and Canuto, O. (2023). The Greenback-Renminbi Tango: The Impacts of Argentina’s Potential Dollarization on its Relations with China, Coverage Heart for the New South, Coverage Temporary PB – 39/23, October
Otaviano Canuto, based mostly in Washington, D.C, is a former vp and a former government director on the World Financial institution, a former government director on the Worldwide Financial Fund, and a former vp on the Inter-American Improvement Financial institution. He’s additionally a former deputy minister for worldwide affairs at Brazil’s Ministry of Finance and a former professor of economics on the College of São Paulo and the College of Campinas, Brazil. Presently, he’s a senior fellow on the Coverage Heart for the New South, a professorial lecturer of worldwide affairs on the Elliott College of Worldwide Affairs – George Washington College, a nonresident senior fellow at Brookings Establishment, a professor affiliate at UM6P, and principal at Heart for Macroeconomics and Improvement.
Amshika Amar is an Affiliate Fellow, Centre for Social and Financial Progress. Beforehand, she has labored with the World Financial institution Group in varied world practices.
* The authors want to thank Abdelaaziz Ait Ali for feedback on an earlier model, with out implicating him in any method.